The RECLAIM Healing Protocol, developed by Sri Amit Ray, integrates physical, mental, and spiritual practices to optimize autophagy and mitophagy, critical cellular processes for maintaining health and combating disease. Represented by the acronym RECLAIM (Ray + Exercises + Chanting + Lifestyle + Autophagy + Intermittent Fasting + Meditation), this protocol synergistically combines diverse disciplines to promote cellular renewal. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of each component, detailing its implementation, underlying mechanisms, and scientific rationale, supported by peer-reviewed evidence, positioning the protocol as a promising strategy for enhancing cellular health and longevity.

Introduction
Autophagy, the lysosomal degradation of damaged or superfluous cellular components, and mitophagy, the selective removal of dysfunctional mitochondria, are pivotal for cellular homeostasis (Mizushima & Komatsu, 2011). These processes recycle cellular materials to provide energy and building blocks under stress conditions, while mitigating oxidative damage linked to aging, neurodegeneration, cancer, and metabolic disorders (Palikaras et al., 2018). Dysregulation of autophagy and mitophagy contributes to cellular senescence and disease progression, underscoring the need for interventions that enhance these mechanisms.
Mitophagy is a specialized form of autophagy (cellular self-cleaning) focused on degrading damaged mitochondria. Since mitochondria are the "powerhouses" of the cell—producing ATP, the body’s energy currency—their quality directly influences energy levels, aging, and disease resistance.
The RECLAIM Healing Protocol, developed by Sri Amit Ray, integrates ancient spiritual practices with modern scientific principles to amplify autophagy and mitophagy. This article elucidates the protocol’s components, their practical application, and their mechanistic contributions to cellular renewal, supported by current scientific evidence. The protocol’s holistic approach addresses the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and spiritual health, offering a novel framework for health optimization.
The RECLAIM Protocol
Ray - Wisdom and Meanings in Life
The RECLAIM protocol is anchored in the wisdom of Sri Amit Ray, a spiritual teacher, pioneer of the 114-chakra system, and compassionate artificial intelligence, who integrates ancient wisdom with modern scientific insights. This component emphasizes the fusion of Ray’s neuro-spiritual teachings, particularly his chakra-based framework, with the body’s innate biological intelligence. Primarily focused on bringing more energy, and a deeper sense meaning in life.
Practitioners engage in mindfulness and intention-setting practices, focusing on aligning the 114 chakras—energy centers believed to regulate physiological and psychological functions—through guided visualizations and affirmations that connect spiritual awareness with cellular processes.
These practices may modulate neuroendocrine pathways, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, reducing stress hormones like cortisol that impair autophagy. Research on mind-body interventions, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction, demonstrates reduced cortisol levels and enhanced expression of genes linked to cellular repair, including those involved in autophagy (Black & Slavich, 2016).
By harmonizing neuro-spiritual insights with biological mechanisms, this component fosters a synergistic environment for cellular renewal, potentially amplifying the protocol’s effects on autophagy and mitophagy (Epel & Lithgow, 2014).
Exercises - OM Ananda Tandava Mitophagy Activation Exercises
Physical activities within the RECLAIM protocol include mindful practices such as yoga, tai chi, and qigong, selected for their ability to enhance cellular health through moderate physical stress and mindful movement. Practitioners engage in daily sessions lasting 10-20 minutes, Om Ananda Tandava HIIT exercise, or yoga, tai chi’s flowing sequences to promote flexibility, strength, and mental focus. These exercises induce mild cellular stress, activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of autophagy, while enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and function.
Sri Amit Ray also introduced the Om Ānanda Tāṇḍava HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) exercise, which places the body under temporary energy stress through short bursts of exertion (e.g., 25 seconds) followed by rest (e.g., 15 seconds). This stress triggers:
- AMPK activation: An energy sensor that turns on autophagy and mitophagy pathways.
- PGC-1α activation: A master regulator that stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis.
- SIRT1 activation: A gene that supports healthy aging, fat metabolism, and DNA repair.
These molecular activations increase the clearance of damaged mitochondria and promote the growth of new, more efficient ones. What distinguishes Om Ānanda Tāṇḍava from other HIIT protocols is the integration of mantra, breath, and spiritual consciousness into every cycle. Chanting “Om” while moving, or holding the awareness of bliss ("ānanda") during rest intervals, activates vagal tone, reduces inflammation, and brings the autonomic nervous system into balance—an essential environment for healing and mitochondrial repair.
Studies demonstrate that aerobic and resistance exercises upregulate autophagic flux in skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissues, reducing oxidative stress and supporting mitophagy (He et al., 2012). For example, exercise-induced autophagy is mediated by the upregulation of LC3-II and Beclin-1, critical autophagic markers, in muscle tissues (Lira et al., 2013). Additionally, mindful movement practices improve blood flow and oxygen delivery, optimizing mitochondrial efficiency and cellular energy metabolism, which are critical for preventing age-related cellular decline (Crane et al., 2013).
Chanting - Applications of Healing Sound Vibrations
Chanting, rooted in spiritual traditions, involves the rhythmic repetition of mantras or sacred sounds, often drawn from Ray’s teachings on vibrational healing. Practitioners dedicate 15–30 minutes daily to chanting specific mantras, such as “Om” or chakra-specific sounds, in a meditative setting to enhance relaxation and focus. This practice reduces cortisol levels, which can inhibit autophagy when chronically elevated, and may influence cellular function through vibrational or neuroendocrine effects.
Research indicates that chanting modulates the parasympathetic nervous system, lowering stress-induced inflammation and upregulating genes associated with cellular longevity, such as SIRT1 (Kaliman et al., 2014). A study on mantra chanting found reduced markers of oxidative stress and improved heart rate variability, suggesting a supportive role in cellular health (Bernardi et al., 2001). By creating a state of physiological calm, chanting fosters an environment conducive to autophagic and mitophagic processes, complementing the protocol’s other components.
Lifestyle - Habit Patterns That Supports Healing
The lifestyle component encompasses daily habits that support cellular renewal, including a nutrient-rich diet, adequate sleep, and stress management. Practitioners follow a diet emphasizing autophagy-supporting foods, such as polyphenol-rich fruits (e.g., blueberries, pomegranates), omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., salmon, flaxseeds), and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, kale), which provide antioxidants and cofactors for autophagic pathways. Sleep is prioritized, with 7–9 hours nightly to facilitate cellular repair and mitochondrial quality control.
Stress management techniques, such as journaling or mindfulness, are integrated to maintain hormonal balance. Research shows that dietary polyphenols, like resveratrol, activate sirtuins, proteins linked to autophagy and longevity (Baur & Sinclair, 2006). Adequate sleep supports mitophagy by regulating circadian rhythms and reducing oxidative stress, with studies demonstrating that sleep deprivation impairs autophagic flux (Xie et al., 2013). Stress reduction mitigates cortisol’s inhibitory effects on cellular renewal, creating a robust foundation for the protocol’s efficacy (Sapolsky, 2004).
Awareness of Autophagy and Mitophagy
As the central focus of the RECLAIM protocol, autophagy represents the cellular self-cleaning process that recycles damaged organelles and proteins. While not directly practiced, autophagy is amplified through the synergistic effects of exercise, intermittent fasting, and meditation. These components collectively activate pathways such as AMPK and inhibit the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), key regulators of autophagic flux.
By clearing cellular debris and maintaining energy homeostasis, autophagy prevents the accumulation of damaged components linked to diseases like Alzheimer’s, cancer, and diabetes (Levine & Kroemer, 2019). For instance, autophagy enhancement has been shown to reduce amyloid-beta accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease models (Nixon, 2013). The protocol’s integrated approach ensures sustained autophagic activity, leveraging the cumulative impact of its components to optimize cellular health and resilience.
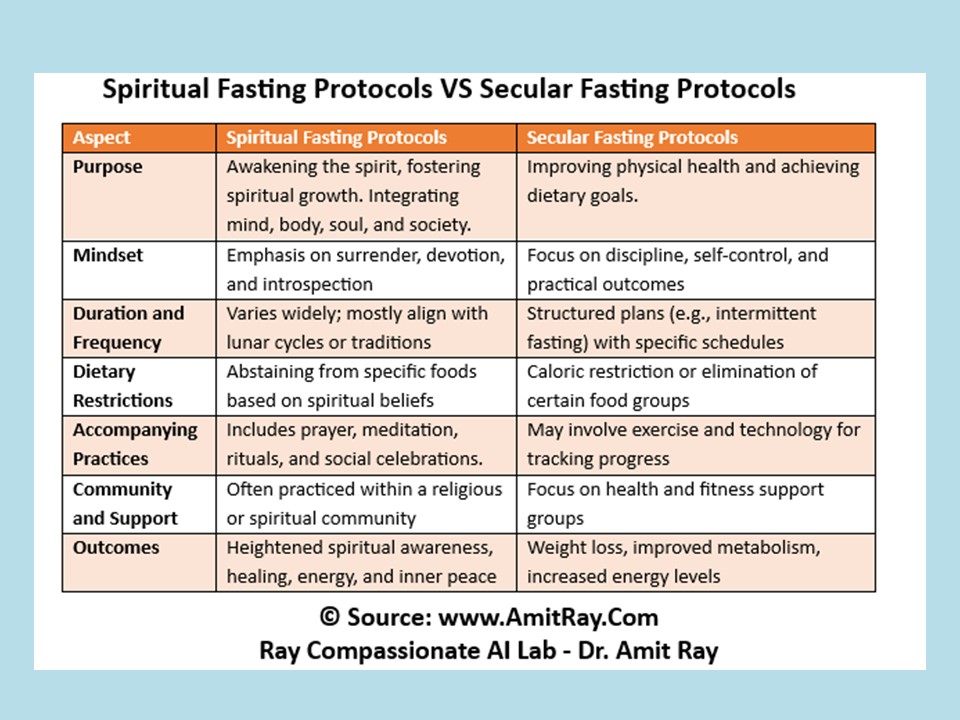
Intermittent Fasting / Ekadashi Fasting or Spiritual Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) involves structured cycles of eating and fasting, typically following the 16/8 method (16 hours fasting, 8 hours eating) or alternate day fasting. Similarly, Ekadashi Fasting or other Spiritual Fasting provides mind, body, spirit total healing.
Practitioners fast overnight and into the morning, consuming nutrient-dense meals within a designated window, such as 12 PM to 8 PM. This practice depletes glycogen stores, activating AMPK and inhibiting mTOR, which triggers autophagy and mitophagy.
Research confirms IF’s role in enhancing cellular renewal, with benefits in metabolic health, neuroprotection, and longevity (Mattson et al., 2017). A clinical trial demonstrated that IF increases autophagic markers like LC3-II and reduces oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome patients (Harvie et al., 2011). IF also improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation, further supporting mitochondrial function and cellular homeostasis (Patterson & Sears, 2017). The protocol’s structured fasting schedule ensures consistent activation of these pathways, enhancing the overall impact on cellular health.
Meditation
Meditation, encompassing the Ray 114 chakra meditation, mindfulness, visualization, and mantra-based practices, is a cornerstone of the RECLAIM protocol, often guided by Ray’s spiritual teachings. Practitioners engage in daily sessions of 12–24 minutes in a quiet environment, focusing on techniques such as mindful breathing, chakra visualizations, or affirmations.
These practices reduce stress hormones like cortisol, which can suppress autophagy, and upregulate genes associated with cellular longevity, such as SIRT1 and FOXO3 (Buric et al., 2017). Meditation enhances parasympathetic activity, promoting relaxation and reducing inflammation, which supports autophagic and mitophagic processes. A randomized controlled trial found that mindfulness meditation reduces inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein, indirectly supporting cellular health (Creswell et al., 2012). By fostering a mind-body connection, meditation amplifies the protocol’s holistic impact on cellular renewal.
Mechanisms of Action
The RECLAIM protocol enhances autophagy and mitophagy through interconnected physiological mechanisms. Exercise and intermittent fasting activate AMPK and inhibit mTOR, shifting cellular metabolism toward autophagic flux and mitochondrial biogenesis (He et al., 2012; Mattson et al., 2017).
Nutrient-rich diets provide substrates like polyphenols and omega-3s, which upregulate sirtuins and other autophagy-related proteins (Baur & Sinclair, 2006). Chanting and meditation reduce stress-induced cortisol, mitigating its inhibitory effects on autophagy, and influence gene expression via the HPA axis (Kaliman et al., 2014; Buric et al., 2017). Sleep and lifestyle practices optimize circadian rhythms and hormonal balance, supporting mitochondrial quality control (Xie et al., 2013). Collectively, these mechanisms create a cellular environment conducive to efficient cleanup and renewal, addressing both autophagic and mitophagic pathways.
Evidence and Research
While direct studies on the RECLAIM protocol are in process, however, its components are supported by robust scientific evidence, as detailed above. Future research should investigate the protocol’s integrated effects in clinical settings, particularly its impact on disease-specific outcomes and biomarkers of cellular health, such as LC3-II, p62, and mitochondrial DNA content. Longitudinal studies could assess its efficacy in preventing age-related diseases and optimizing longevity.
Practical Application
A sample daily RECLAIM routine includes:
- Morning: 12 to 24 minutes of chakra-focused meditation and mantra chanting, followed by 45 minutes of yoga or tai chi.
- Day: A 16/8 fasting schedule, with meals between 12 PM and 8 PM, emphasizing polyphenol-rich foods, omega-3s, and low-glycemic carbohydrates.
- Evening: 15 minutes of light stretching and mindfulness practice, followed by 7–9 hours of sleep in a dark, quiet environment.
This regimen ensures the harmonious integration of all components, maximizing their impact on autophagy and mitophagy. Practitioners may adjust the intensity and duration based on individual needs, guided by Ray’s teachings or trained facilitators.
Discussion
The RECLAIM protocol’s holistic design offers a promising approach to preventing diseases associated with impaired autophagy, such as Alzheimer’s, cancer, and diabetes (Levine & Kroemer, 2019; Nixon, 2013). Its integration of physical, nutritional, and spiritual practices addresses multiple dimensions of health, potentially surpassing the efficacy of single-modality interventions. However, challenges include individual variability in response, the need for adherence to a multifaceted regimen. Future studies should explore the protocol’s efficacy in diverse populations, quantify its effects on autophagic and mitophagic biomarkers, and assess its feasibility in clinical and community settings.
Conclusion
The Sri Amit Ray RECLAIM Healing Protocol represents a pioneering framework for enhancing autophagy and mitophagy, leveraging the synergy of physical, mental, and spiritual disciplines to promote deep cellular renewal. By integrating Ray’s neuro-spiritual insights with evidence-based practices, it offers a comprehensive strategy for optimizing health and longevity. Further research is warranted to validate its efficacy and refine its application, positioning RECLAIM as a transformative approach in preventive and integrative medicine.
References
-
- Baur, J. A., & Sinclair, D. A. (2006). Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 5(6), 493–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2060
- Bernardi, L., Sleight, P., Bandinelli, G., Cencetti, S., Fattorini, L., Wdowczyc-Szulc, J., & Lagi, A. (2001). Effect of rosary prayer and yoga mantras on autonomic cardiovascular rhythms: Comparative study. BMJ, 323(7327), 1446–1449. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.323.7327.1446
- Black, D. S., & Slavich, G. M. (2016). Mindfulness meditation and the immune system: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1373(1), 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12998
- Buric, I., Farias, M., Jong, J., Mee, C., & Brazil, I. A. (2017). What is the molecular signature of mind–body interventions? A systematic review of gene expression changes induced by meditation and related practices. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 670. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00670
- Crane, J. D., MacNeil, L. G., & Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2013). Exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis and its role in metabolic health. Sports Medicine, 43(7), 555–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0044-5
- Creswell, J. D., Irwin, M. R., Burklund, L. J., Lieberman, M. D., Arevalo, J. M., Ma, J., Breen, E. C., & Cole, S. W. (2012). Mindfulness-based stress reduction training reduces loneliness and pro-inflammatory gene expression in older adults: A small randomized controlled trial. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 26(7), 1095–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.006
- Epel, E. S., & Lithgow, G. J. (2014). Stress biology and aging mechanisms: Toward understanding the deep mechanisms of mind–body interventions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(Supplement 2), 17136–17143. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1409238111
- Harvie, M. N., Pegington, M., Mattson, M. P., Frystyk, J., Dillon, B., Evans, G., Cuzick, J., Jebb, S. A., Martin, B., Cutler, R. G., Sonntag, W. E., Maudsley, S., Carlson, O. D., Egan, J. M., Flyvbjerg, A., & Howell, A. (2011). The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: A randomized trial in young overweight women. International Journal of Obesity, 35(5), 714–727. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.171
- He, C., Sumpter, R., & Levine, B. (2012). Exercise induces autophagy in peripheral tissues and in the brain. Autophagy, 8(10), 1548–1551. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.21327
- Kaliman, P., Alvarez-López, M. J., Cosín-Tomás, M., Rosenkranz, M. A., Lutz, A., & Davidson, R. J. (2014). Rapid changes in histone deacetylases and inflammatory gene expression in expert meditators. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 40, 96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.11.004
- Levine, B., & Kroemer, G. (2019). Biological functions of autophagy genes: A disease perspective. Cell, 176(1-2), 11–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.048
- Lira, V. A., Okutsu, M., Zhang, M., Greene, N. P., Laker, R. C., Breen, D. M., Hoehn, K. L., & Yan, Z. (2013). Autophagy is required for exercise training-induced skeletal muscle adaptation and improvement of physical performance. The FASEB Journal, 27(10), 4184–4193. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-228486
- Mattson, M. P., Longo, V. D., & Harvie, M. (2017). Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Research Reviews, 39, 46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.005
- Mizushima, N., & Komatsu, M. (2011). Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell, 147(4), 728–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.026
- Nixon, R. A. (2013). The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nature Medicine, 19(8), 983–997. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3232
- Palikaras, K., Lionaki, E., & Tavernarakis, N. (2018). Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nature Cell Biology, 20(9), 1013–1022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0176-2
- Patterson, R. E., & Sears, D. D. (2017). Metabolic effects of intermittent fasting. Annual Review of Nutrition, 37, 371–393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
- Sapolsky, R. M. (2004). Why zebras don’t get ulcers: The acclaimed guide to stress, stress-related diseases, and coping (3rd process. ed.). Holt Paperbacks.
- Xie, L., Kang, H., Xu, Q., Chen, M. J., Liao, Y., Thiyagarajan, M., O’Donnell, J., Christensen, D. J., Nicholson, C., Iliff, J. J., Takano, T., Deane, R., & Nedergaard, M. (2013). Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science, 342(6156), 373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
- Ray, Amit. "Spiritual Fasting: A Scientific Exploration." Yoga and Ayurveda Research, 4.10 (2024): 75-77. https://amitray.com/spiritual-fasting-a-scientific-exploration/.
- Ray, Amit. "Anandamide Bliss Meditation: The Science and Spirituality of the Bliss Molecule." Compassionate AI, 4.12 (2024): 27-29. https://amitray.com/anandamide-meditation/.
- Ray, Amit. "Autophagy During Fasting: Mathematical Modeling and Insights." Compassionate AI, 1.3 (2025): 39-41. https://amitray.com/autophagy-during-fasting/.
- Ray, Amit. "Autophagy, Inflammation, and Gene Expression During Dawn-to-Dusk Navratri Fasting." Compassionate AI, 1.3 (2025): 90-92. https://amitray.com/autophagy-during-dawn-to-dusk-navaratri-fasting/.
- Ray, Amit. "Autophagy in AI: Destructive vs. Constructive." Compassionate AI, 2.4 (2025): 42-44. https://amitray.com/autophagy-in-ai/.
- Ray, Amit. "Autophagy Fasting: Definition, Time Hour, Benefits, and Side effects." Compassionate AI, 2.4 (2025): 57-59. https://amitray.com/autophagy-fasting-definition-time-hour-benefits-and-side-effects/.
- Ray, Amit. "Ekadashi Fasting and Healthy Aging: A Mathematical Model." Compassionate AI, 2.5 (2025): 93-95. https://amitray.com/ekadashi-fasting-and-healthy-aging-a-mathematical-model/.
- Ray, Amit. "Sri Amit Ray’s RECLAIM Healing Protocol for Autophagy and Mitophagy." Yoga and Ayurveda Research, 2.6 (2025): 21-23. https://amitray.com/reclaim-healing-protocol-framework-for-autophagy-mitophagy/.